Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs, Problems, Reliability
Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs, Problems, Reliability : Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs
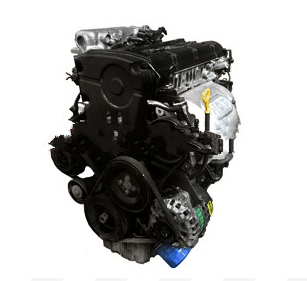
Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs, Problems, Reliability. The G4GC engine is the greatest engine of the Beta II series. Its predecessor is the G4GF produced given that 1997. The two-liter G4GC engine is completely new. The G4GC engine has many upgraded and completely new parts.
The engine has the cast iron cylinder block, the brand-new crankshaft with eight counterweights, more powerful linking rods, and reshaped pistons. The engine has DOHC 16-valve aluminum cylinder head. The intake camshaft is equipped with variable valve timing system CVVT. There are no hydraulic lifters in this engine. You require to adjust valve gaps every 60,000 miles (100,000 km). If you will hear some knocking sounds; possibly it is a big valve space, do not worry. The engine valvetrain uses the timing belt (keep an eye on its condition).
Here is essential info on Engine, Hyundai, 2.0 elantra, Beta II, beta II engine, G4GC, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine problems, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine reliability, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine specs, issue, kia 2.0, oil, power, problem, problems, reliability, specs. We have the cool resources for Engine, Hyundai, 2.0 elantra, Beta II, beta II engine, G4GC, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine problems, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine reliability, Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine specs, issue, kia 2.0, oil, power, problem, problems, reliability, specs. Check it out for yourself! You can gather Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs guide and read the latest Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs, Problems, Reliability.
| Title | Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs |
|---|---|
| Format | PNG |
| Width | 307px |
| Height | 281px |
| URL | https://uscarsnew.com/wp-content/uploads/Hyundai-KIA-G4GC-2.0L-Engine-Specs.png |
| Published Date | October 30, 2021 |
| Latest Updated Date | October 30, 2021 |
| Uploaded By | Karen R. Russell |
Back To Hyundai KIA G4GC 2.0L Engine Specs, Problems, Reliability